Making Vet Exams Easier with Basic Obedience
Enhancing Understanding and Collaboration
Interpreting Animal Stress Signals
Recognizing subtle signs of animal distress improves handling during medical procedures. Ear position, tail carriage, and facial tension all communicate an animal's comfort level. Skilled interpretation of these signals allows for timely intervention before stress escalates, creating safer experiences for both animals and handlers. A calm animal responds better to examination and treatment.
For instance, flattened ears combined with tense muscles typically indicate discomfort, while relaxed posture suggests receptivity to handling. This knowledge transforms veterinary interactions, making them less stressful for all involved.
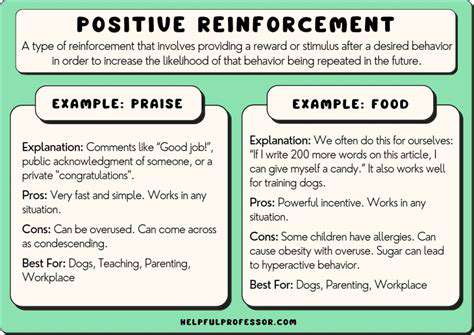
Reward-Based Behavior Shaping
Positive reinforcement methods focus on encouraging desirable responses through pleasant consequences. This approach builds positive associations with medical handling, making future visits progressively easier. When animals learn that calm behavior leads to rewards, they become more cooperative patients.
Strategic use of treats, praise, or favorite toys motivates animals to tolerate necessary procedures. Consistent positive experiences establish trust and willingness to participate in examinations, medication administration, and other healthcare needs.
Establishing Predictable Patterns
Familiar routines significantly reduce animal anxiety. Maintaining consistent pre-visit rituals, travel methods, and clinic protocols helps animals anticipate what comes next. This predictability provides psychological comfort during potentially stressful medical encounters.
Structured routines help animals feel more secure in clinical environments. Familiar elements like specific carriers, travel routes, or handling techniques create continuity between home and medical settings.
Gradual Exposure Techniques
Systematic desensitization involves slowly introducing animals to medical stimuli while maintaining positive experiences. This method proves particularly valuable for animals with previous negative healthcare encounters. Starting with brief, low-intensity exposures and gradually increasing duration and complexity helps rebuild confidence.
When combined with rewards, this approach can transform an animal's perception of medical care from threatening to neutral or even positive. Many behavior specialists recommend this method for animals with significant medical anxiety.
Proper Restraint Methods
Appropriate handling techniques minimize stress during examinations. Loose leads allow animals some movement freedom, reducing tension, while proper positioning ensures safety for both patient and handler. Understanding species-specific handling needs prevents unnecessary distress.
The Value of Steady Progress
Behavior modification requires patience and persistence. Rushing the process often backfires, while consistent, positive experiences yield lasting results. Each animal progresses at its own pace, and respecting individual differences leads to better long-term outcomes.
Customizing approaches based on an animal's personality and history creates the most effective training plans. Steady, positive reinforcement establishes durable positive associations with medical care.
Lifelong Advantages of Behavioral Training

Building Enduring Therapeutic Relationships
Quality healthcare extends far beyond isolated clinical encounters. Developing trusting patient-provider relationships forms the foundation for effective chronic condition management and preventive care. This requires providers to listen attentively, demonstrate empathy, and consider each patient's complete life context. When patients feel genuinely heard, they engage more actively in their care plans.
Personalized Healthcare Strategies
Optimal outcomes emerge from care plans tailored to individual circumstances. Generic approaches often miss critical personal factors that influence health behaviors and treatment responses. Comprehensive understanding of each patient's unique situation allows for more effective, sustainable interventions that patients can realistically implement.
Considering Life Context Factors
Social and environmental circumstances profoundly impact health outcomes. Healthcare providers must account for these real-world factors when designing treatment plans. Incorporating social service support when needed helps address practical barriers to care adherence and health maintenance.
Developing Patient Self-Sufficiency
Teaching patients to manage their conditions promotes long-term success. When individuals understand their health status and have practical self-care skills, they become active partners in maintaining wellness. Effective patient education adapts to varying learning styles and literacy levels for maximum comprehension and retention.
Leveraging Digital Health Tools
Modern technology enhances continuous care between visits. Patient portals, remote monitoring, and telehealth platforms facilitate ongoing communication and support. These digital solutions help maintain care continuity and prompt attention to emerging concerns. When integrated thoughtfully, technology bridges gaps in traditional healthcare delivery.
Ongoing Health Monitoring
Regular check-ins allow for timely plan adjustments as needed. Continuous evaluation catches subtle changes early, preventing minor issues from becoming major complications. These scheduled touchpoints also reinforce the therapeutic relationship, reminding patients they have consistent professional support.
Read more about Making Vet Exams Easier with Basic Obedience
Hot Recommendations
- The Impact of Early Socialization on a Dog's Interaction with Other Animals
- Car Travel and Puppy Socialization: Making the Journey a Positive Experience
- The Importance of Early Environmental Exposure for Puppy Development
- Taking Your Puppy to the Vet: Positive Socialization Strategies
- Making Training a Positive Experience for Your Puppy
- Public Transportation and Puppy Socialization: A Step by Step Guide
- Safe Socialization: Allowing Others to Pet Your Puppy
- Helping a Puppy Who Struggles with "Stay"
- Positive Puppy Interactions: Making Meetings with New Friends Fun
- No Treats Needed? Training Basic Commands with Verbal Praise