Too Many Distractions: Training Sit, Lie Down, and Stay in Challenging Environments
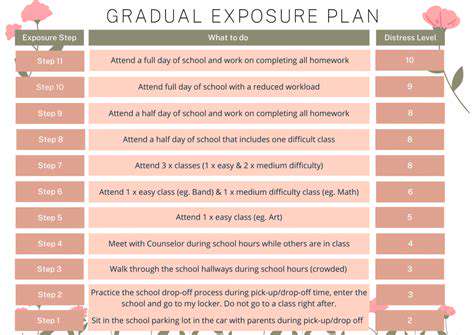
This evidence-based therapeutic approach systematically reduces fear responses through gradual exposure. Clinicians have successfully applied these principles across diverse populations, from veterans with PTSD to children with specific phobias. The method's effectiveness stems from its ability to rewire maladaptive fear responses while maintaining the patient's sense of safety.
Neuroscientific studies demonstrate that repeated controlled exposure actually modifies amygdala reactivity, the brain's fear center. Patients completing structured desensitization programs show measurable changes in brain scans, with decreased activation in fear circuits and increased prefrontal cortex engagement.
Components of a Desensitization Hierarchy
Effective hierarchies carefully balance challenge and safety. Therapists often spend multiple sessions constructing personalized exposure ladders with input from patients. A typical arachnophobia hierarchy might begin with viewing cartoon spiders, progress to photographs, then videos, before culminating in controlled live interactions. Each rung represents a 10-15% increase in anxiety provocation - small enough to remain manageable.
Developing Coping Mechanisms
Contemporary therapy integrates multiple evidence-based techniques during exposure. Patients might employ diaphragmatic breathing, cognitive restructuring, or grounding exercises during challenging steps. This multipronged approach addresses both physiological and psychological aspects of anxiety, creating more robust and generalizable coping skills.
Addressing Underlying Issues
Comprehensive treatment explores developmental origins of maladaptive fears. Many phobias originate from traumatic experiences or learned behaviors during childhood. Processing these underlying narratives often accelerates desensitization progress and reduces relapse rates.
The Importance of Gradual Exposure
The pacing of exposure significantly impacts outcomes. Rushing the process risks retraumatization, while excessively slow progression may reinforce avoidance. Skilled therapists continuously monitor subjective distress levels, adjusting the hierarchy as needed. This dynamic approach maintains therapeutic momentum while respecting individual tolerance thresholds.
Ethical Considerations and Safety Protocols
Reputable clinics maintain strict ethical guidelines for exposure therapy. These include obtaining informed consent, establishing clear safety signals, and having crisis protocols in place. Therapists must balance therapeutic challenge with compassion, ensuring patients never feel coerced into intolerable situations.
Practical Training Techniques for Distracted Environments
Minimizing External Distractions
Creating optimal learning spaces requires both physical and digital boundary-setting. High-performing organizations design training areas with sound-dampening materials, adjustable lighting, and ergonomic furnishings. Many now implement focus hours where all non-essential communications are suspended to protect concentration.
Utilizing Focus Techniques
The Pomodoro Technique's effectiveness stems from its alignment with human attention spans. Research suggests most adults maintain peak focus for 20-50 minute intervals. Advanced practitioners often customize work/break ratios based on individual chronotypes and task demands.
Developing Concentration Skills
Regular mindfulness practice physically alters brain structure. MRI scans reveal increased gray matter density in the prefrontal cortex of long-term meditators - the region governing focus and impulse control. Even brief daily practice can yield measurable improvements in attention regulation.
Improving Task Management
The Eisenhower Matrix provides a robust framework for prioritization, distinguishing between urgent and important tasks. Modern project management tools like Asana or Trello can visualize workflow, making complex projects more manageable.
Creating a Distraction-Free Learning Environment
Environmental psychology research identifies several key factors for optimal focus spaces: natural lighting (200-500 lux), ambient noise levels (50-60 dB), and controlled temperature (20-23°C). Many tech companies now offer focus pods - soundproofed individual workstations with adjustable environmental controls.
Applying Active Listening Techniques
The RASA framework (Receive, Appreciate, Summarize, Ask) structures effective listening. Training programs incorporating deliberate practice of these skills report 42% improvement in information retention compared to passive listening approaches.
Utilizing Technology for Focus
App developers have created sophisticated focus tools using behavioral psychology principles. Forest app gamifies focus time by growing virtual trees, while Freedom syncs blocks across all devices. These tools leverage our psychological responses to commitment and loss aversion.
Building Confidence and Consistency: Key to Success
Understanding the Role of Focus
Modern neuroscience confirms that focused attention acts as the gateway to skill acquisition. Each undistracted practice session strengthens myelin sheaths around relevant neural pathways. Professionals who maintain consistent, focused practice demonstrate significantly faster expertise development across diverse fields.
Identifying Your Distractions
Conducting a personal distraction audit reveals surprising insights. Many find that internal distractions (wandering thoughts, emotional preoccupations) prove more disruptive than external ones. Keeping a distraction log for several days often uncovers previously unnoticed patterns.
Creating a Focused Environment
The concept of attention residue explains why dedicated workspaces matter. When we frequently switch locations, our brains continue processing aspects of the previous environment. Having a consistent, optimized workspace reduces this cognitive drag.
Developing Effective Time Management Strategies
Time blocking works best when aligned with natural energy rhythms. Tracking personal productivity patterns for a week can reveal optimal windows for different task types. Most people experience peak cognitive performance 2-4 hours after waking.
Practicing Mindfulness and Meditation
Brief mindfulness exercises (even 1-2 minutes) can reset attention capacity. The STOP technique (Stop, Take a breath, Observe, Proceed) serves as an effective focus anchor throughout the day.
Implementing Strategies for Avoiding Distractions
Behavioral economists suggest implementing commitment devices - voluntary restrictions that make distractions harder to access. This might include using a separate browser profile for work or physically distancing tempting devices.
Building Consistency Through Self-Discipline
Willpower functions like a muscle - it fatigues with use but strengthens over time. Establishing consistent routines reduces decision fatigue, conserving mental energy for important tasks. The most successful professionals view discipline not as deprivation, but as skillful self-management.