Preparing Your Puppy for Veterinary Visits Through Socialization
Early Exposure and Socialization
The formative years of childhood serve as a pivotal window for cultivating social awareness. During this phase, young minds start constructing their worldview through daily interactions. These initial experiences act as invisible architects, quietly shaping how children will engage with society for decades to come. Through countless moments of shared laughter, tears, and discovery, children unconsciously absorb social blueprints from their environment.
Socialization during these tender years plants seeds for crucial life skills - the ability to understand unspoken emotions, work collaboratively, and express thoughts clearly. These competencies become the bedrock upon which all future relationships are built, from playground friendships to professional networks. The confidence gained through positive early interactions often determines whether children approach new social situations with curiosity or apprehension.
Building Blocks of Attachment
Psychological research consistently highlights how early bonds create emotional templates. When caregivers provide reliable comfort and support, children develop an internal compass for healthy relationships. This security allows them to venture into unfamiliar social territories, knowing a safe harbor awaits their return. Such stability fosters emotional intelligence that proves invaluable during life's inevitable challenges.
The constancy of a trusted adult's presence teaches children that the world can be predictable and kind. This lesson in reliability becomes the foundation for developing patience, emotional regulation, and conflict resolution skills. Over time, these nurtured abilities blossom into the emotional resilience needed to navigate adulthood's complexities.
The Role of Play in Social Development
Far from being mere entertainment, childhood play functions as a sophisticated training ground. Through make-believe scenarios and shared games, children experiment with social dynamics in low-stakes environments. These playful interactions serve as rehearsal spaces where young minds practice reading social cues and testing boundaries. The sandbox becomes a classroom, and toy-sharing transforms into a masterclass in compromise.
During imaginative play, children unconsciously mirror observed behaviors while adding creative twists. This natural mimicry represents one of humanity's most effective learning mechanisms, passing down social knowledge across generations. Whether pretending to run a store or care for dolls, children refine their understanding of social roles and responsibilities.
Cultural Influences on Socialization
Every society cultivates distinct social expectations that shape developing minds. From communication styles to emotional expression, cultural norms create invisible frameworks that guide behavior. Recognizing these diverse social blueprints helps us appreciate the rich tapestry of human interaction. Children absorb these cultural lessons through everyday rituals, family traditions, and community celebrations.
The transmission of cultural values occurs through countless subtle moments - how elders are addressed, how conflicts are resolved, how joy is expressed. These lived experiences gradually construct a child's understanding of their place within larger social structures. This cultural programming enables children to function effectively within their specific communities while potentially limiting their understanding of alternative social paradigms.
The Impact of Early Socialization on Future Outcomes
The social skills nurtured during childhood's formative years often determine life trajectories. Well-socialized individuals typically demonstrate greater academic persistence, professional adaptability, and emotional intelligence. Children who develop robust interpersonal skills carry an invisible advantage, navigating life's challenges with greater ease and resilience. These foundational abilities influence everything from college admissions interviews to marital harmony.
Conversely, early social deprivation or trauma can create lasting obstacles to meaningful connection. Without intervention, negative socialization patterns may perpetuate across generations, creating cycles of social anxiety and relational dysfunction. Early identification and support for socialization challenges can dramatically alter these trajectories, offering hope for positive change.
Introducing New Stimuli in a Controlled Environment
Introducing Controlled Stimuli for Puppy Socialization
Thoughtful exposure to novel experiences forms the cornerstone of confident canine development. This deliberate approach allows young dogs to build positive associations with the unfamiliar. The key lies in maintaining absolute control over the environment and stimuli intensity, ensuring each new encounter remains below the fear threshold. Properly executed, this method creates resilient companions comfortable with life's unpredictability.
Gradual Exposure and Positive Reinforcement
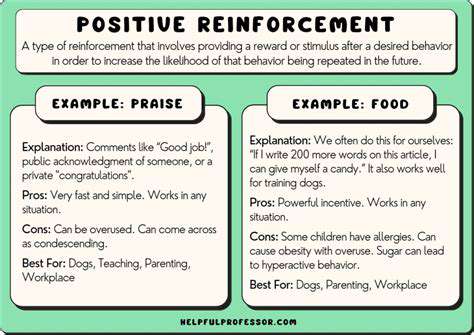
The most effective socialization follows the principle of incremental challenge. Begin with stimuli so mild they barely register, then slowly increase intensity as confidence grows. For sound sensitivity, this might mean starting with recorded noises played at whisper volume across the room. Pair each exposure with high-value rewards, creating neural pathways that associate novelty with pleasure rather than threat.
Identifying Potential Triggers and Fears
Astute observation forms the foundation of successful socialization. Canine body language speaks volumes through subtle shifts - averted gaze, lip-licking, or sudden stillness often precede more obvious fear signals. Recognizing these early warning signs allows for immediate course correction, preventing negative experiences from taking root in the puppy's memory.
Utilizing Familiar Tools for Comfort
Anchor items provide psychological security during challenging exposures. A well-loved chew toy or blanket soaked in familiar scents can lower stress hormones significantly. These comfort objects serve as transitional security blankets, bridging the known and unknown until confidence develops.
Creating a Safe and Predictable Space
The ideal training environment eliminates unnecessary variables. A quiet, enclosed space with controlled access allows complete focus on the specific stimulus being introduced. Consistency in location helps establish mental routines, while removing environmental surprises keeps the puppy's attention where it belongs.
The Importance of Patience and Consistency
Canine socialization follows biological timetables that resist rushing. Neural pathways strengthen through repetition and positive association, requiring methodical patience. Maintaining identical protocols across training sessions builds reliable expectations, while irregular approaches create confusion and undermine progress.
Addressing Potential Challenges and Re-introducing Stimuli
When setbacks occur, the wise handler immediately reduces pressure. Forced exposure to frightening stimuli often worsens fear responses. Instead, return to previously mastered levels and rebuild gradually, allowing the puppy's confidence to recover fully before progressing again.

Modern prosthetic technology has entered a revolutionary phase, with traditional materials giving way to advanced alternatives. Carbon fiber innovations have transformed limb replacements into featherlight yet astonishingly durable extensions that move with unprecedented naturalism. These material breakthroughs directly translate to improved quality of life, offering users both enhanced mobility and psychological comfort.

Read more about Preparing Your Puppy for Veterinary Visits Through Socialization
Hot Recommendations
- The Impact of Early Socialization on a Dog's Interaction with Other Animals
- Car Travel and Puppy Socialization: Making the Journey a Positive Experience
- The Importance of Early Environmental Exposure for Puppy Development
- Taking Your Puppy to the Vet: Positive Socialization Strategies
- Making Training a Positive Experience for Your Puppy
- Public Transportation and Puppy Socialization: A Step by Step Guide
- Safe Socialization: Allowing Others to Pet Your Puppy
- Helping a Puppy Who Struggles with "Stay"
- Positive Puppy Interactions: Making Meetings with New Friends Fun
- No Treats Needed? Training Basic Commands with Verbal Praise