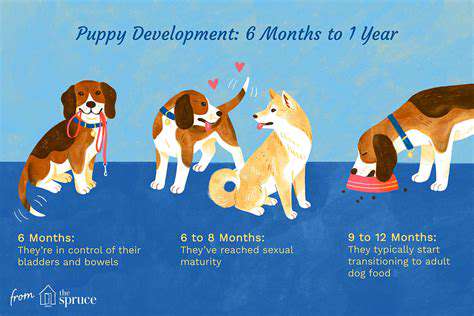
Making Obedience Training a Game for Your Puppy
This exploratory thinking does more than enhance the immediate task - it builds flexible thinking skills that transfer to all areas of life. When people practice seeing problems from various perspectives, they develop cognitive agility that serves them well beyond any single activity.
Cultivating a Positive Learning Environment
Playful instruction creates an atmosphere where mistakes become learning opportunities rather than failures. In this environment, participants feel safe to experiment and push boundaries. The resulting sense of accomplishment fuels continued engagement and builds authentic confidence that isn't dependent on perfect outcomes.
Such environments produce resilient learners who approach challenges with curiosity rather than apprehension. When people associate learning with positive emotions, they develop lifelong habits of self-improvement and knowledge-seeking.
Adapting to Diverse Learning Styles
Effective playful instruction accounts for different processing styles. Visual thinkers thrive when concepts include diagrams or storyboards. Auditory learners engage deeply with verbal explanations or musical mnemonics. Hands-on learners need physical components they can manipulate. The most successful approaches weave multiple modalities together.
This personalized approach ensures all participants can access the material in ways that make sense to them. When people receive information through their preferred channels, retention and application improve dramatically.
Born Jacob Rubenstein in 1911, the man who would become infamous as Jack Ruby led a life that was anything but ordinary. His early career path meandered through various jobs, from selling novelties to operating nightclubs, each experience adding another layer to his complex personality.
Enhancing Recall with a Tug-of-War-Style Approach
Understanding the Tug-of-War Analogy
Memory functions much like an actual tug-of-war, with various cognitive processes competing for dominance. Effective memory strategies require balancing these forces to create optimal recall conditions. The strongest memories emerge from this dynamic tension between storage and retrieval systems.
Active Recall as One Team
Active recall represents the deliberate effort to retrieve information. This mental exertion creates stronger neural connections than passive review, much like physical exercise builds muscle through resistance. Each successful retrieval reinforces the memory pathway, making future access easier.
Spaced Repetition as Strategic Planning
Strategic timing of review sessions mimics the ebb and flow of a well-played match. The intervals between sessions should challenge but not overwhelm the memory system. This spacing effect takes advantage of how our brains naturally consolidate information over time.
Interleaving as a Shifting Force
Mixing different but related concepts creates beneficial confusion that strengthens learning. This technique forces the brain to identify distinguishing features between similar ideas, creating more precise memory traces. The initial difficulty leads to more durable and flexible knowledge.
Elaboration: Building a Stronger Rope
Creating meaningful connections transforms isolated facts into networked knowledge. The more associations a memory has, the more retrieval routes exist. This web of connections makes information resistant to forgetting and easier to access from multiple angles.
Mnemonics: Extra Help in the Tug-of-War
Memory aids provide clever shortcuts for challenging information. Well-designed mnemonics create vivid, unusual associations that stand out in our memory landscape. These mental hooks make retrieval faster and more reliable, especially for complex or abstract material.
Retrieval Practice: Testing Your Grip
Regular self-testing strengthens recall ability more than additional study time. This practice reveals exactly what you know versus what you only recognize, allowing targeted improvement. The effort required during retrieval actually enhances the memory itself, not just our ability to access it.