Introducing Your Puppy to People Wearing Hats and Sunglasses
Why is this Important?
Understanding Puppy Socialization
Introducing your new puppy to a diverse range of people, sights, and sounds is crucial for their overall development and well-being. Early socialization experiences help shape a puppy's confidence and ability to interact appropriately with the world around them. This process establishes positive associations with various stimuli, preventing anxieties and fears from developing later. A well-socialized puppy is more likely to adapt to new environments and situations with ease, leading to a happier and more well-adjusted dog.
Exposure to different individuals, including those wearing hats and sunglasses, is a fundamental part of this socialization. It helps the puppy learn that these are not threatening or unusual, and that interaction with these individuals is perfectly normal. This early exposure prevents the development of potential phobias or anxieties, which can be difficult to overcome later.
The Impact of Hats and Sunglasses on Puppy Perception
Puppies perceive the world differently than humans. Hats and sunglasses can appear as unusual or intimidating objects, especially if they are paired with unfamiliar facial expressions. Introducing your puppy to individuals wearing these items early on allows them to become accustomed to these novel stimuli, and to associate them with positive interactions. The puppy learns that hats and sunglasses are not inherently dangerous or threatening, and this helps them develop a broader understanding of human behavior.
The shapes and colors of hats and sunglasses can also be stimulating visual experiences for puppies, encouraging curiosity and exploration. This exploration can be beneficial for cognitive development, as well as fostering a more confident and adaptable nature.
Practical Tips for Introducing Your Puppy
When introducing your puppy to people wearing hats and sunglasses, start in a low-stress environment. Choose a familiar and calm setting, where your puppy feels comfortable and secure. Allow the interaction to be on your puppy's terms, and don't force any interaction if the puppy shows signs of discomfort. Positive reinforcement, such as treats and praise, can be used to encourage positive associations with these stimuli.
Gradually increase the complexity of the interactions, such as introducing more people wearing hats and sunglasses, or people wearing these items while interacting with other people. Remember to observe your puppy's body language carefully. Signs of stress, such as lip licking, yawning, or tucked tails, indicate that the interaction should be paused or ended. Consistency and patience are key to ensuring a positive experience for your puppy.
Long-Term Benefits of Exposure
The long-term benefits of exposing your puppy to people wearing hats and sunglasses extend far beyond simply getting used to these items. It fosters a more adaptable and confident dog, who is better equipped to handle a wide range of situations. This early socialization helps your puppy develop strong social skills, reducing the likelihood of behavioral problems in the future. This broader exposure to various stimuli allows your puppy to develop into a well-rounded and happy companion.
A well-socialized puppy is better able to navigate new environments and meet new people with confidence and grace. This translates to a more enjoyable experience for both the puppy and the people around them, ensuring a harmonious relationship throughout their lives.
Gradual Exposure is Key
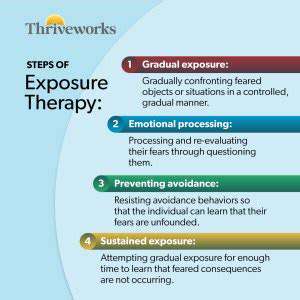
Understanding the Concept
Gradual exposure therapy is a cornerstone of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for anxiety and phobias. It involves systematically exposing individuals to feared stimuli, situations, or objects in a controlled and measured manner. This controlled exposure allows for the gradual desensitization to the feared triggers, ultimately reducing the anxiety response.
The key here is slow and steady progress, not overwhelming the individual with intense exposure from the outset. This approach is designed to help the person learn to manage and cope with anxiety-provoking situations in a safe and supportive environment.
Building a Hierarchy of Exposure
A crucial aspect of gradual exposure is constructing a hierarchy of feared stimuli. This involves creating a ranked list of situations, objects, or thoughts that evoke different levels of anxiety. Starting with the least anxiety-provoking item, individuals can systematically work their way up the hierarchy, facing increasingly challenging situations. This allows for a controlled and manageable progression, ensuring that each step is within the individual's current coping capacity.
Controlling the Intensity and Duration
Careful control of the intensity and duration of exposure is paramount. This involves carefully selecting the specific level of exposure that elicits a moderate anxiety response. Overwhelming the individual with intense exposure too quickly can hinder progress and potentially worsen anxiety. By carefully controlling these elements, therapists can promote a safe and manageable experience, encouraging the individual to learn to tolerate and manage their anxiety.
Gradual increases in exposure intensity and duration are key to effective desensitization. This approach allows the individual to develop coping mechanisms and build resilience over time, leading to a reduction in fear and anxiety.
Addressing Underlying Thoughts and Beliefs
Gradual exposure therapy isn't just about facing feared situations; it also addresses the underlying thoughts and beliefs that contribute to anxiety. This involves exploring the negative thought patterns and challenging their validity. This cognitive restructuring component works in tandem with the behavioral exposure to provide a comprehensive approach to overcoming anxiety disorders.
By understanding and modifying the maladaptive thought patterns that fuel anxiety, individuals can develop a more balanced perspective and reduce the intensity of their fear responses.
Importance of Therapist Support
Throughout the gradual exposure process, the consistent support of a qualified therapist is essential. Therapists provide guidance, reassurance, and support to help individuals navigate the challenges and anxieties they encounter. Their presence ensures the process remains safe and effective, fostering a sense of trust and control. The therapist plays a crucial role in monitoring the individual's progress, adjusting the exposure strategy as needed, and offering encouragement to maintain motivation.
Furthermore, therapists can help identify and address any potential setbacks or obstacles that may arise during the exposure process, ensuring that the individual receives the necessary support and guidance.
Addressing Fearful Behaviors
Understanding the Root of Fear
Fearful behaviors in puppies, particularly around people wearing hats and sunglasses, often stem from a combination of factors. These might include past negative experiences, a lack of positive socialization, or simply a natural apprehension towards unfamiliar stimuli. Understanding the specific trigger, whether it's the shadow cast by a hat or the reflective glare of sunglasses, is crucial to developing an effective training strategy.
Identifying the precise cause allows you to tailor your approach, whether it's desensitization, counter-conditioning, or a combination of both, to help your puppy overcome their fear. Early intervention is key to preventing the fear from escalating into a more significant problem.
Desensitization Techniques
Desensitization gradually introduces the feared stimulus, in this case, people wearing hats and sunglasses, in a controlled and positive manner. Start with a person wearing a hat or sunglasses at a distance where your puppy doesn't react negatively. Reward calm, neutral behaviors with treats and praise. Gradually decrease the distance while maintaining a positive response. This process requires patience and consistency; it is not a quick fix.
Counter-Conditioning Strategies
Counter-conditioning pairs the feared stimulus with a positive experience. For instance, if your puppy fears a person wearing a hat, associate that person with something your puppy enjoys, like a favorite toy or tasty treats. The goal is to replace the fear response with a positive emotional response. This strategy requires careful observation of your puppy's reactions and adjustment of the strategy as needed.
Positive Reinforcement Training
Consistent positive reinforcement is paramount in addressing fearful behaviors. Use high-value treats and enthusiastic praise to reward calm and neutral responses to people wearing hats and sunglasses. Avoid punishment, as this can exacerbate fear and create a negative association. Positive reinforcement builds trust and encourages desired behaviors.
Socialization Opportunities
Socialization is crucial for shaping positive responses. Exposing your puppy to various people wearing hats and sunglasses in controlled environments, like dog parks or community events, will help them get accustomed to the sights and sounds. Ensure that the interactions are positive and enjoyable. It's crucial to start with short, positive encounters and gradually increase the duration and complexity of the social interactions.
Gradual Exposure and Building Confidence
Gradually increasing exposure to the stimulus is vital for desensitization. Start with a person wearing a hat from a distance, then gradually decrease the distance and increase the time spent interacting. Each step should be met with positive reinforcement. This gradual exposure helps your puppy build confidence and trust, reducing their fear response.
Importance of Patience and Consistency
Addressing fearful behaviors in puppies requires patience and consistency. Rushing the process can be counterproductive. Celebrate small victories and maintain a calm and reassuring demeanor throughout the training process. Remember that every puppy is different, and the time it takes to overcome fear varies. Be prepared to adjust your strategy based on your puppy's individual needs and responses.
Read more about Introducing Your Puppy to People Wearing Hats and Sunglasses
Hot Recommendations
- The Impact of Early Socialization on a Dog's Interaction with Other Animals
- Car Travel and Puppy Socialization: Making the Journey a Positive Experience
- The Importance of Early Environmental Exposure for Puppy Development
- Taking Your Puppy to the Vet: Positive Socialization Strategies
- Making Training a Positive Experience for Your Puppy
- Public Transportation and Puppy Socialization: A Step by Step Guide
- Safe Socialization: Allowing Others to Pet Your Puppy
- Helping a Puppy Who Struggles with "Stay"
- Positive Puppy Interactions: Making Meetings with New Friends Fun
- No Treats Needed? Training Basic Commands with Verbal Praise