Creating Positive Associations: Treats and Praise in Puppy Socialization
Size appropriateness directly impacts safety and nutritional efficacy. Oversized pieces pose aspiration risks, while undersized morsels may fail to deliver sufficient caloric value. Continuous supervision during treat consumption remains essential to monitor chewing patterns and prevent potential obstructions.
Ingredient awareness proves equally critical. Some juveniles exhibit sensitivities to specific components, necessitating careful label examination. Introduce novel treats gradually while observing for adverse reactions—discontinue immediately if signs of intolerance emerge and consult your veterinary professional.
Strategic Timing with Treats and Praise

Strategic Timing for Maximum Impact
Precision timing when delivering rewards significantly enhances training efficacy. The critical window for reinforcement lasts approximately 1.5 seconds—delayed rewards weaken behavior associations exponentially. This temporal sensitivity applies universally, from fundamental commands to complex behavioral shaping.
Individual learning styles dictate optimal approaches. High-value rewards administered precisely as paws touch the floor during a sit command create indelible neural pathways. This instantaneous feedback mechanism accelerates skill acquisition while maintaining engagement.
Utilizing High-Value Treats Strategically
Premium rewards—like freeze-dried liver or cheese crumbles—prove invaluable for distractible learners. These biological motivators capture attention more effectively than standard kibble, particularly in challenging environments.
Reserving special rewards for breakthrough moments creates powerful learning accelerants. Deploy them when introducing novel commands or reinforcing behaviors in high-distraction settings to cement neural connections.
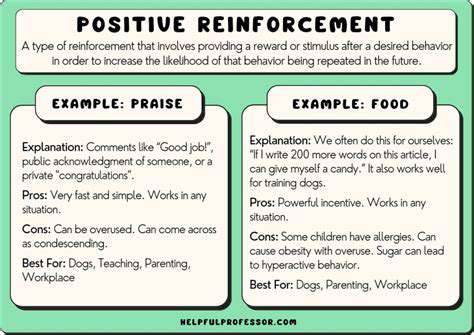
Positive Reinforcement as a Core Principle
Modern behavioral science emphasizes reward-based methodologies. This approach strengthens desired actions through pleasant consequences rather than suppressing unwanted behaviors through aversion.
Constructive training environments foster mutual trust while producing more durable behavioral modifications. The resulting cooperative dynamic often yields superior long-term results compared to punitive approaches.
The Role of Patience and Consistency
Canine learning follows an irregular trajectory. Expect plateaus and occasional regression—consistent application of principles ultimately yields proficiency. Short, frequent sessions with clear expectations prove more effective than marathon training attempts.
Celebrate incremental progress rather than demanding immediate perfection. This measured approach maintains motivation while accommodating individual learning curves.
Combining Treats with Other Positive Reinforcement
While edible rewards serve as powerful motivators, diversifying reinforcement maintains engagement. Tactile praise, verbal markers, and interactive play each contribute unique motivational dimensions.
Multimodal reinforcement systems prevent habituation while addressing various canine motivational drivers. This comprehensive approach enhances learning while deepening the human-canine bond.
While isolation exercises serve specific purposes, compound movements drive comprehensive forearm conditioning. Multi-joint exercises like pull-ups and deadlifts generate substantial forearm activation through dynamic stabilization demands. This integrated approach ensures balanced development within functional movement patterns.
Beyond Treats: The Importance of Praise
Beyond the Immediate Gratification: Why Praise Matters
While edible rewards provide immediate motivation, sustained behavioral change requires emotional reinforcement. Affectionate touch, enthusiastic vocalizations, and joyful body language create lasting positive associations that transcend treat dependency.
Verbal acknowledgment of minor successes—like momentary eye contact or voluntary check-ins—strengthens the human-canine bond. These micro-reinforcements accumulate into significant behavioral shaping over time.
The Power of Specific Praise: Tailoring Your Reinforcement
Precision praise (Beautiful heel position!) proves more effective than generic approval. This targeted feedback clarifies expectations while reinforcing exact desired behaviors.
Specific verbal markers help canines discriminate between similar actions, accelerating the learning process. This linguistic precision becomes increasingly valuable when teaching complex behavioral chains.
Building Trust and Confidence through Consistent Praise
Predictable positive responses to desired behaviors create psychological safety. This security enables bolder exploration of new skills and environments, fostering well-adjusted companions.
Confidence-building praise should emphasize effort rather than perfection, particularly during initial learning phases. This approach cultivates resilience when facing novel challenges.
The Ripple Effect of Positive Reinforcement: Shaping Long-Term Behavior
Consistent praise establishes neural pathways that influence overall temperament. Dogs raised with abundant positive reinforcement typically demonstrate greater adaptability and problem-solving capacity.
This reinforcement style creates virtuous cycles—each positive interaction increases the likelihood of future cooperation, ultimately yielding more harmonious coexistence.
Making Socialization Fun: Creating a Positive Environment
Creating a Welcoming Atmosphere
Effective socialization spaces balance stimulation with comfort. Zoned areas accommodating different interaction styles (active play versus quiet observation) prevent sensory overload while encouraging gradual participation.
Environmental cues like non-slip flooring and sound-dampening materials reduce stress triggers, particularly for noise-sensitive individuals.
Encouraging Active Participation
Scaffolded activities—beginning with parallel engagement before progressing to direct interaction—help hesitant participants build confidence. Structured games with clear rules provide social frameworks for uncertain dogs.
Understanding Diverse Needs
Recognize that socialization readiness varies by individual. Force-free approaches respecting each dog's comfort level yield more sustainable results than forced interactions.
Facilitating Meaningful Interactions
Quality trumps quantity in canine socialization. Brief, positive encounters with appropriate partners prove more valuable than prolonged stressful gatherings.
Addressing Potential Challenges
Proactive management prevents negative experiences. Visual barriers, controlled introductions, and exit strategies allow graceful disengagement when needed.
Promoting a Culture of Respect
Clear communication of expectations prevents misunderstandings. Teach appropriate greeting protocols and reinforce calm interactions from all participants.
Utilizing Technology Effectively
While digital tools can supplement socialization, prioritize real-world experiences. Video demonstrations may prepare dogs for novel situations, but live practice remains irreplaceable.